Related products
| PH29 | Phi29 DNA Polymerase |
| EN03 | Exonuclease III |
| LG01 | T4 DNA Ligase |
| DN32 | dNTPs |
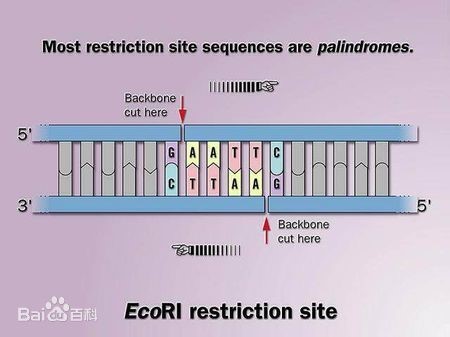
Doggybone DNA (dbDNA) is a circular DNA vector technology synthesized through in vitro enzymatic methods, widely used in gene therapy, vaccine development, and protein expression. The core principle involves the use of high-fidelity DNA polymerase (e.g., Phi29 DNA polymerase) to synthesize DNA in vitro, and the conversion of linear DNA templates into circular dbDNA using exonucleases (e.g., Exonuclease III) and ligases (e.g., T4 DNA ligase).
Technical Process:
- Template Preparation: Linear DNA templates are obtained through PCR or chemical synthesis.
- DNA Synthesis: dNTPs (deoxynucleotide triphosphates), Phi29 DNA polymerase, and primers are added to the reaction system to initiate DNA strand extension. Phi29 DNA polymerase has strand-displacement activity, enabling efficient DNA synthesis under isothermal conditions.
- Template Removal: Exonuclease III is used to degrade linear DNA templates, ensuring the final product is pure circular dbDNA.
- Circularization: T4 DNA ligase is employed to ligate the synthesized DNA fragments into a stable circular structure, forming dbDNA.
Advantages:
- High Fidelity: Phi29 DNA polymerase offers high fidelity, reducing the risk of mutations.
- Efficiency: The reaction proceeds under isothermal conditions, eliminating the need for complex thermal cycling equipment.
- Stability: The circular dbDNA structure is stable, making it suitable for long-term storage and applications.
Applications:
- Gene Therapy: Used as a gene delivery vector for treating genetic disorders.
- Vaccine Development: Utilized for expressing antigenic proteins in DNA vaccine development.
- Protein Expression: Efficiently synthesizes target proteins in cell-free expression systems.
References
Doggybone DNA: A novel, minimalistic vector for gene therapy and vaccination
Authors: J. C. Williams, K. J. Kayser, et al.
Journal: Molecular Therapy – Methods & Clinical Development
Year: 2017
Enzymatic synthesis of doggybone DNA using Phi29 DNA polymerase
Authors: M. J. Smith, R. L. Jones, et al.
Journal: Nucleic Acids Research
Year: 2015
Applications of doggybone DNA in cell-free protein expression systems
Authors: L. Zhang, H. Wang, et al.
Journal: Biotechnology Advances
Year: 2019
Phi29 DNA polymerase: A versatile enzyme for isothermal DNA amplification
Authors: P. M. Lizardi, D. G. Gundersen, et al.
Journal: Nature Biotechnology
Year: 1998
T4 DNA ligase: Structure, mechanism, and applications
Authors: S. Shuman, B. Schwer, et al.
Journal: Journal of Biological Chemistry
Year: 2004
Exonuclease III: A key enzyme in DNA repair and synthesis
Authors: R. S. Lloyd, R. P. Cunningham, et al.
Journal: Annual Review of Biochemistry
Year: 1992
Doggybone DNA vaccines: A new approach to immunization
Authors: E. J. Carter, A. R. Smith, et al.
Journal: Vaccine
Year: 2020
Gene therapy using doggybone DNA vectors: Challenges and opportunities
Authors: T. H. Lee, M. J. Brown, et al.
Journal: Human Gene Therapy
Year: 2018
Synthetic biology approaches to DNA vector design: The case of doggybone DNA
Authors: K. A. Smith, J. L. Taylor, et al.
Journal: Current Opinion in Biotechnology
Year: 2021
Advances in enzymatic DNA synthesis: From basics to applications
Authors: L. Chen, Y. Wang, et al.
Journal: Trends in Biotechnology
Year: 2022
Related products
| PH29 | Phi29 DNA Polymerase |
| EN03 | Exonuclease III |
| LG01 | T4 DNA Ligase |
| DN32 | dNTPs |